
Motor Insurance Decoded: All You Need To Know About Insuring Your Vehicle
India’s roads are considered to be some of the most dangerous in the world, reporting a high number of accidents, deaths and injuries every year. This makes having an insurance cover when venturing out on the roads all the more important and is something that is also mandated by law. However, according to estimates made by the General Insurance Council (GIC), nearly 60 per cent of vehicles plying on India’s roads do not have a valid insurance. Here is what you need to know about motor insurance, its legal requirements and the procedure to file claims.
-
-
-
- Is it necessary to get my vehicle insured?Yes. The Motor Vehicles Act 1988 makes it mandatory for any and all vehicles running on India’s roads (cars, two-wheelers and commercial vehicles like trucks and buses) to have a valid ‘liability only’ or ‘third party’ insurance cover. This means that the insurance policy purchased must cover any potential injuries and damage caused by one’s vehicle to another person or their property.
- Why is motor insurance mandated by law?Motor insurance is generally regarded as something central to road safety and responsibility, ensuring that compensation is provided to victims of road accidents.
- What is the penalty for driving a vehicle which is not insured?Under the Motor Vehicles Act, an individual found driving a vehicle without insurance can be fined ₹1,000 and imprisoned for up to 3 months or both.The Motor Vehicles (Amendment) Bill has proposed increasing this penalty to ₹2,000.
-
-
Read More: 10 Things To Know About The Motor Vehicles (Amendment) Bill 2016
-
-
- What is third party insurance?‘Liability only’ insurance is generally referred to as ‘third party insurance’. This is a basic type of insurance which covers the law’s mandated requirements.
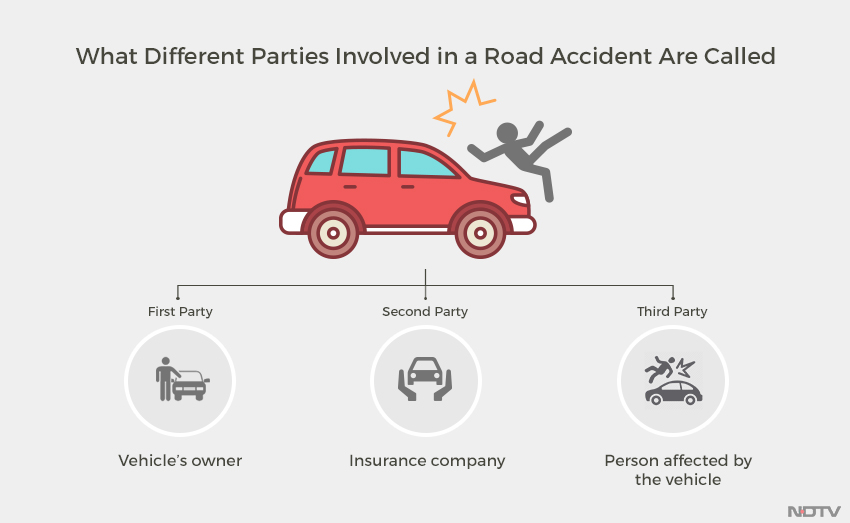 With this type of insurance, when an accident occurs due to the fault of a vehicle’s owner (first party), the insurance company is liable to cover the compensation demanded by the third-party who has been injured or killed, or whose vehicle has been damaged. However, the policyholder will not be a beneficiary of any insurance coverage.On the other hand, a comprehensive insurance bundles together personal damage cover with the third party cover. This allows the claims of both the policyholder and the third party to be looked at.
With this type of insurance, when an accident occurs due to the fault of a vehicle’s owner (first party), the insurance company is liable to cover the compensation demanded by the third-party who has been injured or killed, or whose vehicle has been damaged. However, the policyholder will not be a beneficiary of any insurance coverage.On the other hand, a comprehensive insurance bundles together personal damage cover with the third party cover. This allows the claims of both the policyholder and the third party to be looked at. - What is the procedure for filing a claim?The procedure to make a third party claim is a little complex. The affected individual or their family (third party) must file an FIR and then a case against the vehicle’s owner and their insurer in a Motor Accident Claims Tribunal. This is a special court which particularly deals with claims related to loss of life or property and injury cases which occur due to motor accidents.The court will then decide whether or not the compensation is to be given, as well as the amount.
- How much compensation can be claimed?Under the Motor Vehicles Act, there is no set limit on third party claims. Of course, the final decision on the compensation amount lies with the Motor Accident Claims Tribunal.In practice, while insurers do not set any cap for cases related to death and injury, the cover for third-party property damage generally has a maximum limit of ₹7.5 lakhs, according to the Insurance Regulatory and Development Authority of India (IRDAI). If the amount ruled by the tribunal exceeds this, the policyholder is expected to pay the excess, personally.IRDAI regulations also allow insurers to offer policies that cap the third party property damage cover to ₹6,000, lowering the premium paid by policyholders. Taking this policy does mean that while the premium is lesser, the insurance company will pay no more than ₹6,000 and if the amount to be paid exceeds this, policyholders will have to cover the balance themselves.Interestingly, the pending Motor Vehicles (Amendment) Bill proposes a cap on these claims to ₹10 lakhs for deaths and ₹5 lakhs for serious injuries.
- How is the premium determined?While comprehensive insurance policies vary from company to company, the premium rates for third party insurance are annually set by the IRDAI.For 2016-17, the annual amount set for cars varies between ₹2,055 and ₹6,164. For two-wheelers this ranges from ₹569 to ₹796 while for private commercial goods carrying vehicles it is between ₹7,849 and ₹16,655. The variability of these amounts is based on either the power of the engine or the weight of the vehicle.
- For how long is a motor insurance policy valid?Motor vehicle insurances are generally valid for a year and have to be renewed by paying the annual premium before the expiration date.
- Should the insurance papers be carried in the vehicle at all times?Yes. When one buys a motor insurance policy, Form 51, which is a separate certificate of insurance, is issued in compliance with the Rule 141 of Central Motor Vehicle Rules 1989. This document is what needs to be carried at all times. The rest of the policy papers can be left at home.
- Which companies in India offer motor insurance?There are plenty of motor insurance options in the market to pick from. Be sure to compare what all they have to offer before settling on one. Here are some of the companies that offer policies.Two-wheelers: New India Assurance, IFFCO Tokio, Universal Sompo, Bajaj Allianz, Bharti AXA, HDFC ErgoCars: Bajaj Allianz, Bharti AXA, HDFC Ergo, Liberty Videocon, Tata AIG, Royal SundaramCommercial Vehicles: Bajaj Allianz, Reliance General Insurance, Tata AIG, Royal Sundaram, HDFC Ergo
- What is third party insurance?‘Liability only’ insurance is generally referred to as ‘third party insurance’. This is a basic type of insurance which covers the law’s mandated requirements.
-
Have any other questions about motor insurance? Ask us in the comments below.

















